Assessing the Recent Decline in Drug Overdose Deaths: An Opinion Editorial
The latest CDC report has captured the attention of experts and the public alike as it reveals a significant drop in drug overdose deaths in the United States and Arizona. Over the past year, data has shown a 26.9% decrease nationwide—from 110,037 deaths in 2023 to 80,391 in 2024—marking the lowest overdose fatality rate since 2019. As we work through this complex issue, it is important to examine the multiple factors contributing to this decline, the opportunities offered by key public health interventions, and the challenging twists and turns that still lie ahead.
This opinion editorial explores the various dimensions of this dramatic change, including the roles of enhanced naloxone access, advancements in drug testing methods, improved treatment availability, and emerging patterns in drug supply and usage. By diving into the fine points of each factor, we can get a closer look at how these initiatives interconnect and what the future might hold for overdose prevention efforts.
Understanding the Data: A Detailed Look at the Numbers
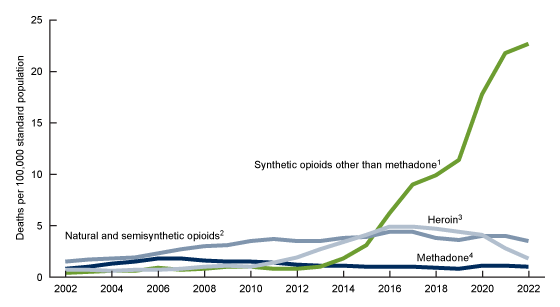
The CDC’s Provisional Drug Overdose Death Counts provide the backbone for our understanding of the current landscape. The report indicates that there were 29,646 fewer overdose deaths in the U.S. in 2024 compared to the previous year. The statistics are even more telling when we break down the numbers for opioids specifically—a decline of 34.2% from 83,140 in 2023 to 54,743 in 2024. These figures include a 36.5% drop in deaths involving synthetic opioids (primarily fentanyl, excluding methadone), alongside declines in deaths linked to cocaine and psychostimulants.
Arizona, while reflecting similar positive trends, experienced a modest 8.7% decrease in overdose deaths—from 2,780 in 2023 to 2,539 in 2024. Regression analysis further underlined a significant though small association (R² = 0.22) between the previous year’s death rate and the percent decline in the current year, indicating that areas with higher overdose rates may just be beginning to see improvements.
State-by-State Variations: A Closer Look at Diverse Outcomes
The decline in overdose deaths, however, was not uniform across all states. While most states experienced reductions, the extent of improvement varied dramatically. For example, West Virginia recorded the largest percentage decline of 43.5%, while Hawaii reported a minimal decline of 0.3%. In contrast, states like Nevada and South Dakota saw small increases of 3.5% and 2.3%, respectively.
This wide range of figures hints at the tangled issues underlying local drug trends and public health strategies. While some states have managed to substantially lower their overdose death numbers, others have faced a mix of challenges ranging from enforcement practices to public health funding allocations.
| Region | 2023 Overdose Deaths | 2024 Overdose Deaths | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States (Overall) | 110,037 | 80,391 | -26.9% |
| Arizona | 2,780 | 2,539 | -8.7% |
| West Virginia | N/A | N/A | -43.5% |
| Hawaii | N/A | N/A | -0.3% |
| Nevada | N/A | N/A | +3.5% |
| South Dakota | N/A | N/A | +2.3% |
Enhanced Access to Naloxone: A Critical Tool in Overdose Prevention
One of the standout elements in reducing overdose deaths is the increased availability and use of naloxone. Naloxone—a drug that rapidly reverses opioid overdoses—has become a must-have tool in emergency overdose situations. Since the end of 2021, nearly every state has authorized licensed pharmacists to dispense naloxone without a prior prescriber visit, making it far easier for communities to access. This change has been pivotal, as studies indicate that naloxone can be the difference between life and death, especially given that seven out of ten drug overdose deaths involve opioids.
Recent data reveals that retail pharmacy-dispensed naloxone prescriptions jumped 122% from 2019 to the fourth quarter of 2023. However, it is important to note that these statistics may understate the true level of outreach because they do not account for naloxone available over-the-counter or distributed via community programs and other non-pharmacy channels.
Increasing Community Outreach and Pharmacy Involvement
The dramatic rise in naloxone prescriptions isn’t solely due to regulatory changes. Many pharmacies and community programs have ramped up their efforts to get naloxone into the hands of individuals who may be at risk of an overdose. This increased availability has made it easier for bystanders, family members, and even peers to rapidly reverse an opioid overdose, thus reducing fatal outcomes substantially.
Key points in the process include:
- Wider authorization protocols, enabling pharmacists to offer naloxone without comprehensive prescriptions.
- Community-based distribution programs which extend reach beyond traditional retail channels.
- An overall heightened public awareness regarding the benefits and usage of naloxone.
These strategies, working together, help lower the number of susceptible individuals facing a fatal opioid event, an essential outcome in our fight against this critical public health challenge.
Fentanyl Test Strips: A Closer Look at Their Impact on Overdose Prevention
Fentanyl test strips have garnered attention as a practical harm reduction tool. Given that fentanyl—a synthetic opioid—has played a large role in the recent rise and subsequent decline of overdose deaths, providing users with the means to detect its presence in illicit drugs is crucial. Legalized in Arizona in May 2021, these strips allow people to test drugs and potentially avoid a fatal overdose by being alerted to the presence of this potent substance.
How Fentanyl Test Strips Work and Save Lives
Fentanyl test strips operate by providing a quick and accessible means to detect fentanyl in a drug sample. When the test strip indicates the presence of the dangerous chemical, users are given the critical information needed to take precautions. This can include using smaller doses or not using the drug at all, as well as seeking help or alerting others to the possible contamination.
Long-term studies and pilot programs in various states have shown that these strips can lead to changes in drug consumption behaviors as users become more cautious. Additionally, the legalization and integration of fentanyl test strips have paved the way for broader harm reduction efforts in many regions.
- Fentanyl test strips act as an early warning signal for users, reducing risk.
- They encourage informed decision-making about dosage and usage settings.
- The strips also facilitate connections to harm reduction services and treatment programs.
By making fentanyl test strips more accessible, communities may continue to see a decrease in overdose deaths, complementing other measures such as increased naloxone availability and enhanced substance use treatment programs.
Expanding Access to Addiction Treatment: A Path Forward
The decline in overdose deaths is not solely the result of immediate overdose reversal measures or drug testing innovations. Enhanced access to drug treatment plays an equally important role. Recent policy measures from the Biden administration have expanded the availability of treatment medications like methadone and buprenorphine, which help ease opioid withdrawal symptoms and reduce overall dependency.
Key Strategies for Improving Treatment Access and Outcomes
In addition to the federal push for increased treatment medication availability, state and local governments have significantly expanded their opioid settlement funding. In 2022 and 2023, U.S. states collectively received more than $6 billion, while Arizona alone received over $97 million—expected to exceed $1 billion over the next 18 years. These funds are being allocated across various programs, such as:
- Residential rehabilitation centers and outpatient counseling facilities
- Medication-assisted treatment initiatives
- Community-based mental health and addiction support services
- Housing, transportation, and legal aid programs as ancillary supports
While the primary focus is on treatment, the intertwined benefits extend to harm reduction efforts and overall public safety. A well-rounded treatment network not only helps prevent immediate overdose deaths but also supports long-term recovery, reducing the pool of people at risk when the supply of illicit drugs remains dangerous.
Lessons from Past Treatment Funding Models
A review of spending patterns from organizations like KFF, Johns Hopkins, and Shatterproof highlights that states have historically allocated approximately 18% of opioid settlement funds to addiction and mental health treatment. Recent experiences underscore the need to not only maintain but also enhance these efforts. Programs that focus on early intervention, outreach, and continuous care have shown promise and could be seen as super important if we are to sustain current declines in drug overdose deaths.
Changes in Drug Supply and Use Patterns: The Shifting Landscape
A critical aspect of understanding the decline in overdose deaths is recognizing the changing patterns in drug supply and usage. The Biden administration has taken steps to limit the export from China of precursor chemicals used in manufacturing fentanyl. While the direct impact of these restrictions remains uncertain, there have been notable changes in drug seizure data reported by U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
How Shifts in Drug Supply Affect Overdose Statistics
Drug seizures have shown mixed patterns over the past few years. For example, fentanyl seizures decreased by 19% in fiscal 2024 after an 83% rise in 2023, whereas cocaine seizures declined by 16% following a 15% increase in the previous year. Interestingly, methamphetamine seizures surged by 24% in 2024 after a 20% dip in 2023. These erratic trends suggest that local enforcement priorities, resource allocation, and even regional drug trafficking networks could be influencing the data as much as actual changes in drug supply.
Some experts argue that in certain regions the drug supply might now contain less fentanyl when mixed with substances such as xylazine, thereby reducing overdose risks. Other theories propose that changes in use patterns—like fewer users shooting alone—could also significantly lower the occurrence of fatal overdoses. Whether these trends are temporary fluctuations or the beginning of a long-lasting shift remains to be seen.
Interpreting Uncertain Trends Amid Enforcement Priorities
While we can identify some correlations between drug seizure trends and overdose rates, it is important to remember that there is no single explanation for the observed decline. Changes in drug supply are just one of many factors at play. Law enforcement efforts, public health interventions, and individual behavior all mix together to create a network of influences that is both full of problems and loaded with promising solutions.
In many ways, this situation presents the typical twists and turns of public health policy in a time of crisis. Decision-makers must be agile, continuously monitoring and adapting to the subtle details of drug markets while ensuring that community-based interventions remain effective and accessible.
Dealing with the Remaining Challenges: Will the Decline Continue?
Despite the encouraging signs of a decline in drug overdose deaths, several challenges remain that could threaten to reverse these gains. While measures such as increased naloxone availability, fentanyl test strips, and expanded treatment access are having a positive impact, the story is by no means complete.
Potential Setbacks and Policy Concerns
A few headwinds could disrupt the progress made so far. Notably, potential cuts to federally funded programs—especially those related to Medicaid and other key substance abuse prevention efforts—could undermine critical support structures. Additionally, recent surveys have indicated that as many as 11% of adults report using illicit opioids, a figure higher than previously estimated, particularly among certain demographic groups such as younger adults, men, and Black respondents.
Such findings remind us that while the immediate overdose statistics have improved, underlying issues remain tense. To ensure sustained success in the battle against overdoses, public health officials must be prepared to work through these complicated pieces of the public health system, addressing both the immediate and long-term drivers of substance abuse.
- Funding sustainability for treatment and harm reduction programs must be prioritized.
- Policymakers need to remain vigilant and responsive to changing drug use patterns.
- The integration of community voices is essential to tailor local interventions effectively.
- Future research should continue to unpack the hidden complexities of these evolving trends.
Learning from the Past to Shape the Future
Historical trends suggest that periods of decline in overdose deaths have sometimes been followed by resurgences, especially when preventive measures are scaled back. It is clear that the decline recorded for 2024 is the product of multiple coordinated efforts rather than a single policy fix. As we look to the future, a continued, comprehensive approach is necessary. Public health programs must be supported not only by sound science but also by persistent political will and community engagement. In other words, ongoing vigilance is required to keep moving in the right direction.
The Broader Impact on Public Health Policy and Community Safety
The recent decline in drug overdose deaths has broader implications for public health policy and community safety. As this trend has garnered national media attention from outlets like CNN, The Washington Post, The New York Times, and PBS Horizon, the message is clear: coordinated public health strategies can indeed save lives. However, these successes also demand ongoing reflection and adaptation at every organizational level.
Integrating Lessons Learned into Future Public Health Strategies
One of the key takeaways from the recent data is that a multiplicity of interventions—ranging from improved access to life-saving medications to better drug testing mechanisms and treatment expansion—can collectively contribute to a substantial decline in overdose deaths. The fine details of these interventions, including the small distinctions in how different states implement policies, provide valuable lessons for other communities facing similar issues. As decision-makers figure a path through this ever-changing landscape, it is crucial to:
- Support and expand existing harm reduction programs with both federal and local funding.
- Enhance interagency collaboration to share best practices and data insights.
- Promote community-driven initiatives that adapt to local needs.
- Continuously evaluate policy impacts using data-driven analyses and feedback from on-the-ground stakeholders.
These actions can help build a more resilient and responsive public health infrastructure, one that not only addresses the immediate crisis but also builds a foundation for long-term community safety and well-being.
Public Perception, Media Coverage, and the Road Ahead
The media’s extensive coverage of these changes plays a key role in shaping public opinion and spurring further policy action. With prominent outlets highlighting the decline despite the lingering challenges, there is a growing sense of cautious optimism among experts and community leaders alike.
Managing Public Expectations Through Clear Communication
It is important for the media, policymakers, and public health officials to communicate the ongoing nature of this issue in a clear, honest manner. While it is certainly encouraging to see significant declines in overdose deaths, these figures must be interpreted in the context of continued risk, particularly for vulnerable populations. Public narratives need to balance praise for recent successes with a sober reminder of the nerve-racking tasks that still lie ahead.
Some practical steps for better public communication include:
- Providing transparent updates on drug overdose statistics and related policies.
- Discussing the subtle details of interventions in an accessible way, using everyday language to describe scientific findings.
- Ensuring that voices of those directly affected by drug misuse and overdose are heard in policy discussions.
This balanced approach can help manage expectations and keep communities engaged with ongoing public health measures, ensuring that progress does not stagnate amidst funding cuts or policy rollbacks.
Reflections on a Year of Change and Future Opportunities
The remarkable decrease in drug overdose deaths in 2024 is a milestone for public health, yet it also serves as a reminder of the ongoing twists and turns in our collective effort to address the overdose crisis. With fewer people at immediate risk and improved intervention mechanisms now in place, we seem to be on a promising path. However, the journey is far from complete.
Opportunities for Further Improvement in Overdose Prevention
Looking forward, there are several opportunities we must seize to maintain and build upon this progress. First, continuous investment in treatment programs is key. With treatment and recovery resources proving to be a linchpin in reducing overdose deaths, policymakers must ensure that financial support does not dwindle in the coming years. Future investments could also focus on:
- Advanced training for medical professionals and first responders to manage overdose emergencies efficiently.
- Broadening access to innovative harm reduction tools and technologies.
- Integrating community-based feedback loops to tailor interventions to the local context.
Second, enhanced collaboration between law enforcement, public health agencies, and community organizations will be essential to adapt quickly to the ever-changing drug market dynamics. By working together, these groups can better figure a path through the confusing bits of drug supply trends and enforcement practices.
Tackling the Remaining Challenges with Resilience
Despite the progress demonstrated in the recent data, several remaining challenges continue to pose a threat. For instance, the potential cutbacks in federally funded programs for substance abuse prevention could quickly reverse positive trends if such financial supports are not maintained. Moreover, the persistent issue of an increasing number of people at risk—evidenced by the recent surge in illicit opioid usage among specific demographic groups—underscores the need for targeted interventions.
Policymakers and healthcare providers must keep addressing these challenges head-on by:
- Continuing education and outreach campaigns that raise awareness about overdose signs and preventive measures.
- Implementing adaptive, data-driven approaches that allow for rapid response to emerging drug trends.
- Ensuring resources are allocated to communities that display persistent high-risk patterns.
By embracing these strategies, we can overcome the intimidating tasks ahead and build upon our recent achievements.
Conclusion: Sustaining Progress and Planning for the Future
The decline in drug overdose deaths marked by the latest CDC report is a promising sign that coordinated public health efforts yield tangible results. From increased access to life-saving naloxone and fentanyl test strips to enhanced addiction treatment programs and targeted policy interventions, a multifaceted approach has led to a significant improvement in public health outcomes.
However, this victory should not spur complacency. The underlying issues—ranging from funding uncertainties to changing drug trafficking dynamics—remain full of problems and demand continuous attention. As we look to the future, it will be super important that policymakers, healthcare providers, and community organizations work together to address both the immediate dangers and subtle details of this crisis.
History teaches us that progress in public health is often marked by a series of challenging pieces along the way. By committing to transparent communication, sustained funding, and data-driven strategies, we can hope to enjoy a lasting decrease in overdose deaths while preparing for potential setbacks. Ultimately, the path forward will require us to figure a path through the intricate landscape of substance abuse, balancing public safety with individual rights and community well-being.
In our opinion, the recent decline in overdose deaths is a testament to what can be achieved when science, policy, and community action work hand in hand. Continued vigilance and adaptation will be necessary as we steer through the nerve-racking challenges ahead. Through collaborative efforts and sustained commitment, we can nurture a public health environment that not only reduces overdose fatalities but also paves the way for healthier, more resilient communities for years to come.
Originally Post From https://azpha.org/2025/06/02/cdc-reports-decline-in-drug-overdose-deaths-in-the-us-az/
Read more about this topic at
CDC Reports Nearly 24% Decline in U.S. Drug Overdose …
‘Unprecedented’ decline in US drug overdose deaths gives …